LAN and WAN
The EZR13T is a standalone networking router with DHCP server and LAN WAN interfaces.
After logging into the router, go to "Network > Interfaces" to view and manage the networking interfaces, including LAN and WAN.
Rx/Tx indicates the real-time data stream instead of the speed. The color on the interface is related to their firewall zones instead of their working status.

LAN
LAN, or local area network, is a technical concept of a virtual interface that distributes internet traffic to all the client devices connected to the extender. It controls the physical LAN port and handles traffic on the WiFi hotspots.
LAN IP
Click the "Edit" button on the first row of the LAN interface to enter the LAN configuration page.
Protocol: Always use the "Static address" protocol for the LAN interface.
IPv4 Address: It's the extender's IP address. It must be compatible with the private IP formats.
IPv4 Netmask: It defines how "large" the LAN network is.
IPv4 Broadcast: The DHCP clients use the broadcast to find and send requests to their servers.
Custom DNS Servers: You can use multiple custom DNS servers to route all the outgoing traffic.

Tab > Physical Settings:
Do not change the Interface settings for normal uses, which should combine "eth0 and wan0-1".
Tab > Firewall Settings:
For regular applications, do not change the default firewall zone of "lan."
When there is more than one extender or router in the same network and working on the same IP range of 192.168.10.x, please change their router IP to a different one to avoid IP conflicts.
Private IP address ranges
Class A: 10.0. 0.0 — 10.255. 255.255
Class B: 172.16. 0.0 — 172.31. 255.255
Class C: 192.168. 0.0 — 192.168. 255.255
DHCP Server
The DHCP server can automatically configure connected devices' TCP/IP settings and lease out an IP address from the available IP pool.
On the LAN interface configuration page, scroll down and find the "DHCP server" section. You can modify the DHCP server settings under the "General Setup" tab.
Ignore Interface: Enable this checkbox will turn off the router's DHCP server. The connected devices will no longer be able to obtain local IP from the router and can not access the mobile internet.
Advanced Settings > Force: Enable this option when there is more than one DHCP server in the entire network.
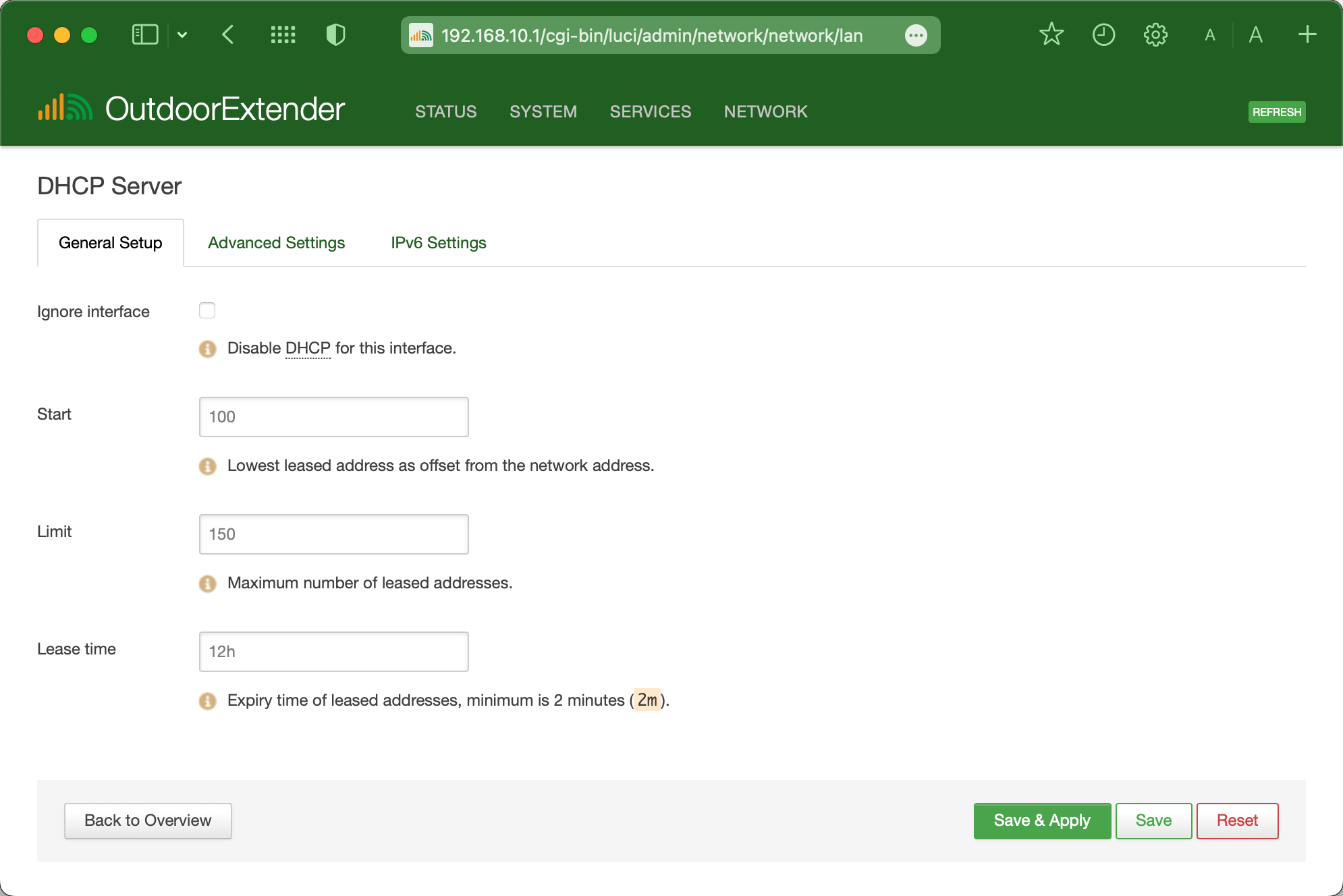
Start
100
The start of the DHCP IP pool.
For example, if the router’s LAN IP is 192.168.10.1 and the netmask is 255.255.255.0, a valid IP address should start with 192.168.10.100.
Limit
150
Define the IP addresses the DHCP server can lease out.
If the start address is 192.168.10.100 and the server can lease out 150, available addresses will be from 192.168.10.100 to 192.168.10.249.
Lease time
12 hours
The duration of an IP lease. Leased-out addresses will expire after the specified period, and a new DHCP lease must be requested. If the device stays connected, its lease will be renewed after half of the limited time passes.
For example, if the lease time is 12 hours, then every 6 hours, the device will send a request to the DHCP server asking to renew its lease.
The lease time can be set in hours (h) or minutes (m). The minimum time that can be specified is 2min (2m). Use Infinite to assign lease time forever.
Static IP Address
If the DHCP server was disabled on the router, we could access the router with a static IP address. Below is an example of static IP address settings. Ensure the gateway IP address and subnet mask address match the router configurations.
Computer IP: 192.168.10.100 (Inside the default DHCP range of 100~249) Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 (also called 24 on Windows) Gateway (Router IP): 192.168.10.1
WAN
WAN stands for Wide Area Network. Technically speaking, the WAN interface on the extender consists of the physical WAN port and WiFi relay link.
The physical WAN port is bound to the "PoE & WAN" port of eth1, which should lead to the PoE injector for inputting a landline internet to the extender.
The WAN interface (eth1) has enabled the DHCP client protocol, and it will automatically obtain the IP address and internet traffic from the target internet sources.

Do not use the same LAN IP address as the target internet source routers. If you must use the same subnet, split them with different IP pools.
Last updated